In contrast, a Systems Framework includes and links multiple layers of temporal and spatial data or information from many different disciplines and from multiple perspectives. Systems Frameworks link and process information across time and space, that include Big Data Analysis processes. Big Data Analysis is the term for a collection of large and complex datasets that are difficult to process or understand using traditional database management tools or data processing applications.
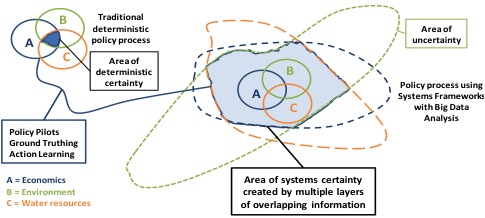
A simple example is provided below for the intersection of Economics (A), Environment (B) and Water Resources (C) considerations in the development of state policy. The traditional deterministic policy process is limited by perceptions of certainty about the data underpinning each of the policy elements. This is defined as the “area of deterministic certainty”.
A conceptual diagram of traditional deterministic policy process and the policy process using Systems Frameworks with Big Data Analysis
The use of Systems Analysis processes allows and frames the Big Data inputs. This results in a wider domain of overlapping data or information from different disciplines. Systems Certainty about policy is provided by the overlapping information. For example, overlapping data from financial costs and economic benefits (A), waterway health and biodiversity (B), and availability of surface water (C) is combined to provide greater understanding of whole of systems outcomes.
The continuing use of the Systems Framework with pilot programs for policy, ground truthing of changes in Big Data in response to actions, and the application of action learning provides a robust process to allow timely application of experimental policy initiatives. This process allows application of feedback loops in the policy process to allow continuous improvement and refinement to maximise value to the whole of society.