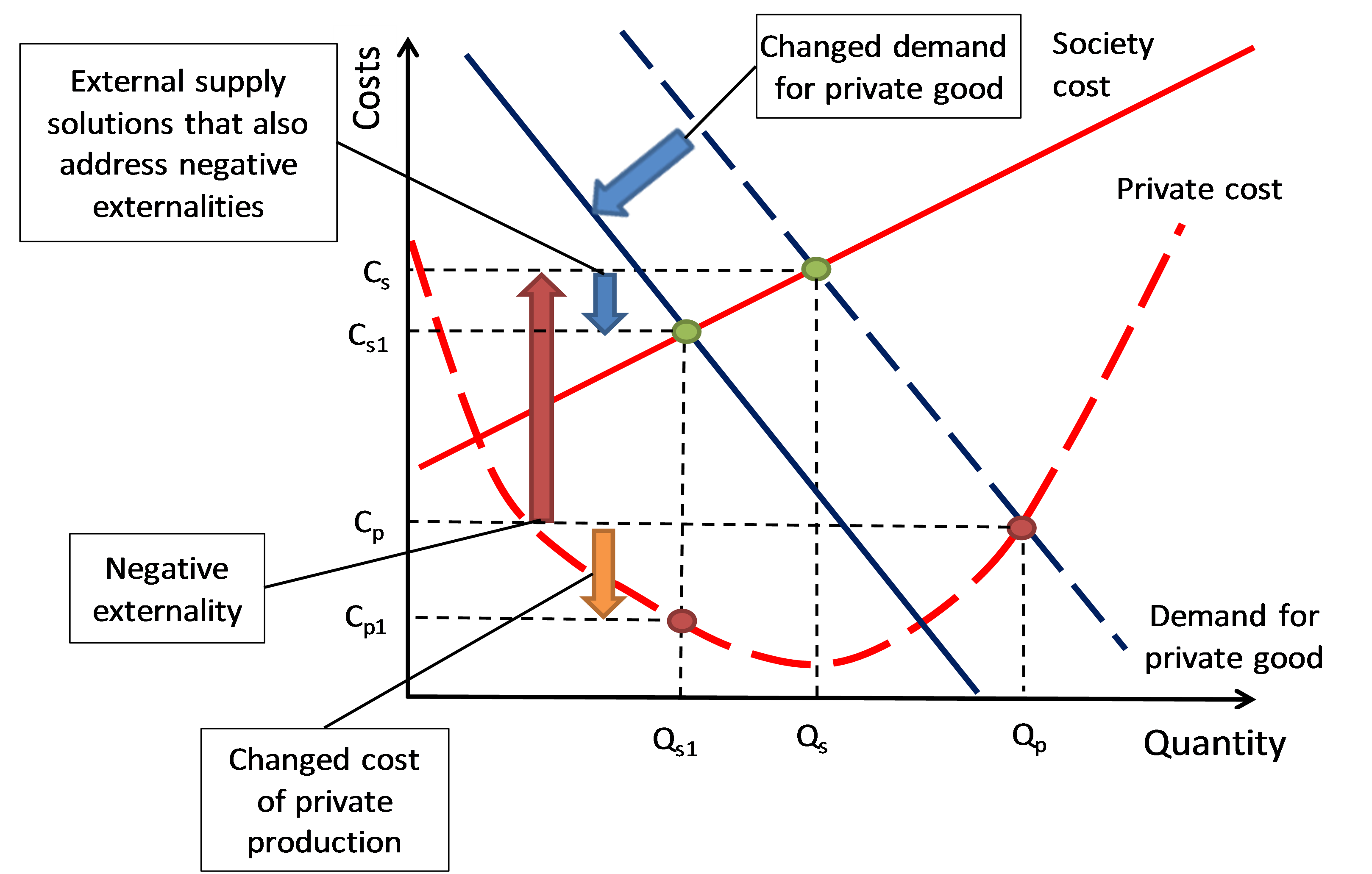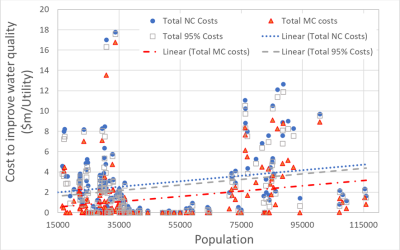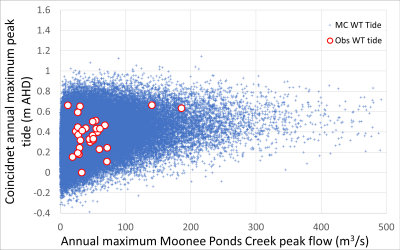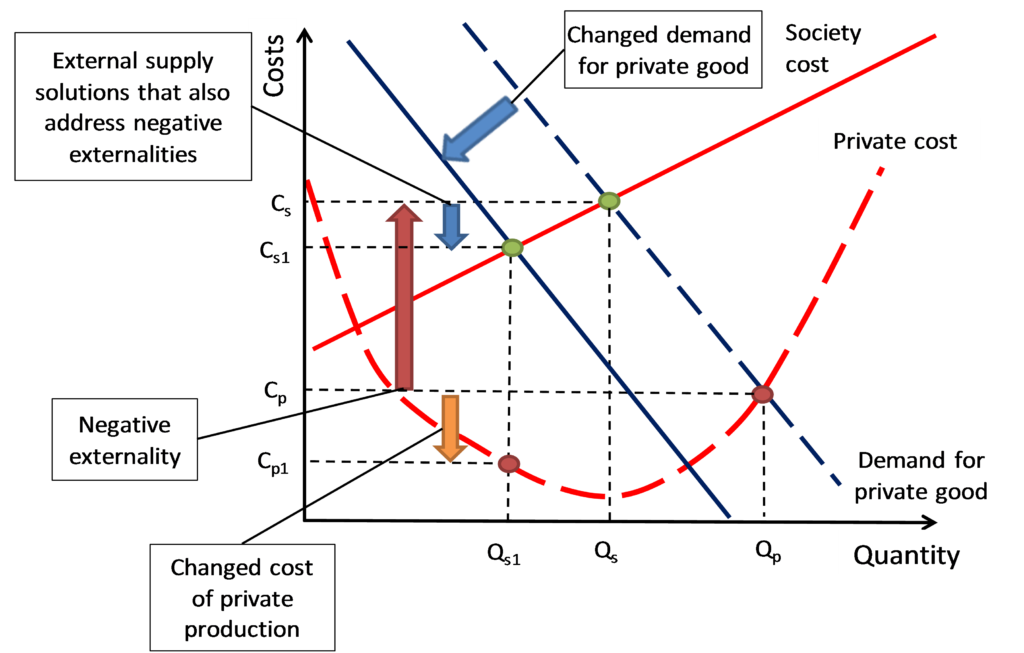
The uncounted negative externalities of private production (supply from water utility) increases society costs and the addition of external solutions (such as demand management and rainwater harvesting) that account for negative externalities reduce society and private costs
Resolving Boundary Conditions in Economic Analysis of Distributed Solutions for Water Cycle Management
Peter J Coombes, Michael Smit and Garth McDonald
Our investigation of the impacts of engineering and economic assumptions on water policy has been published in the Australian Journal of Water Resources.
Over the last 30 years leading thinkers have taken us beyond mechanistic and reductionist analysis into systems theory and the critical boundary judgements that are fundamental to systems analysis. In defining and discussing boundary conditions, we also redefine values and facts that are imposed on hydrological and economic analysis that underpins decisions about government policy in water resources.
The repeal of legislation for distributed interventions (water efficient appliances and rainwater harvesting) that was previously enacted to improve the security of a regional water supply system is examined as a case study. The results of the analysis were defined by the costs and benefits that are inside or outside of the boundaries of legitimate and recognised consideration.
This paper refers to those differences as boundary conditions and considers how those boundary conditions affect the outcome of analysis. Setting of boundary conditions (what is included, what is excluded and assumptions) in engineering and economic analysis dominates outcomes of decisions about government policy.
These insights have general application to development of government water policy.
The investigations outlined in this paper were combined to create an enhanced version of a systems analysis of a policy for setting targets for water savings on all new dwellings. It was established, using appropriate boundary conditions, that a 40% target for water savings is feasible for South East Queensland and provides a cost-benefit ratio of 2.1. These results indicate that a policy of mandating targets for sustainable buildings would provide substantial benefits to the state of Queensland, water utilities and citizens.
Download Paper at: Journal Paper or Journal Paper